Princess Peach™: Showtime! - US Version
17% OffIntroduction
In today’s digital age, networks play a crucial role in connecting devices and facilitating seamless data sharing and collaboration. A network drive is a shared storage space on a network that allows users to access files and folders from multiple devices. Understanding how to find the path of a network drive is essential for efficient file management and productivity. This article will guide you through the process of locating and mapping network drives in various operating systems, along with troubleshooting tips and best practices
Understanding Network Drives
Before delving into the technicalities, let’s grasp the concept of network drives. A network drive is a storage area on a server or a Network-Attached Storage (NAS) device accessible to multiple users over a network. It appears as a drive icon on your computer, much like your local hard drives, and enables you to access files and folders from other computers connected to the same network.
Locating Network Drives
Locating network drives can vary depending on the operating system you are using. In Windows, you can find network drives through File Explorer or by using specific commands in the Command Prompt. On the other hand, Mac users can find network drives through the Finder or by utilizing Terminal commands.
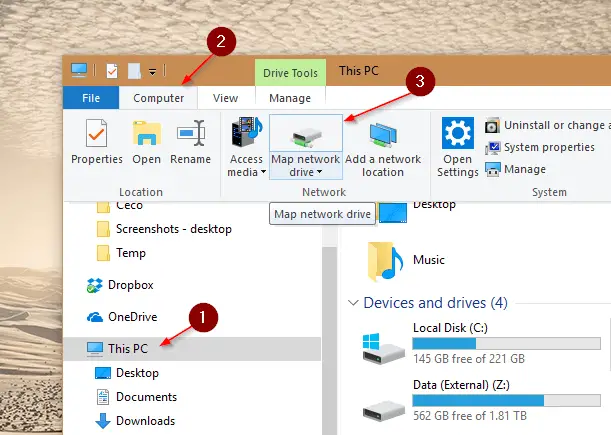
Mapping Network Drives in Windows
Mapping a network drive in Windows allows you to assign a drive letter to the network location for easy access. This section will walk you through the step-by-step process of mapping network drives in Windows, ensuring quick access to your shared files.
Mapping Network Drives in Mac
For Mac users, mapping network drives follows a different approach. By understanding the process of mapping network drives on your Mac computer, you can effortlessly connect to and utilize shared files on the network.
How to find the Mapped Network Drive Share Path:
Mapping a network drive is so easy for all if they do have the correct shared network drive path, few users face issues in finding the network drive share path and this article will help you to find the mapped network drive path.
There is a command called NET USE that is used to list all the shared drives mapped in your computer, to access the command just follow the below-mentioned steps
Steps:
- Click Start and type run and press enter
- Then type “command prompt” or “cmd” in the run command box and press enter
- In the command prompt window type NET USE and press enter, the command will return all the mapped network shared drive paths as shown in the below image.
- Status: Display’s status of the shared drive either OK if it is mapped currently or Disconnected
- Local: Mapped Drive Letter
- Remote: The full path of the shared drive
We can now copy the share drive path from the remote field and use it to map shared drives in other computers.
Network Drive vs. Cloud Storage
Comparing network drives with cloud storage services can help you make an informed decision based on your specific requirements. Understand the differences between these storage solutions and their ideal use cases.
Conclusions
In conclusion, mastering the art of finding the path of a network drive opens up a world of efficient file management and collaboration possibilities. Whether you use Windows or Mac, this article has equipped you with the knowledge to locate, map, and troubleshoot network drives effectively.
FAQs
Q1: Can I access a network drive from a different location?
Yes, as long as you have the necessary network credentials and a stable internet connection, you can access your network drive from virtually anywhere.
Q2: Is cloud-based storage more secure than network drives?
Both cloud-based storage and network drives can be secure when properly configured. However, cloud storage often offers additional security features like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Q3: Can I map multiple network drives on my computer?
Absolutely! You can map multiple network drives on your computer, assigning different drive letters to each mapped location.

Greetings! I am Ahmad Raza, and I bring over 10 years of experience in the fascinating realm of operating systems. As an expert in this field, I am passionate about unraveling the complexities of Windows and Linux systems. Through WindowsCage.com, I aim to share my knowledge and practical solutions to various operating system issues. From essential command-line commands to advanced server management, my goal is to empower readers to navigate the digital landscape with confidence.
Join me on this exciting journey of exploration and learning at WindowsCage.com. Together, let’s conquer the challenges of operating systems and unlock their true potential.